2、History of hypochlorous acid
1. History of hypochlorous acid
The strong sterilization effect of hypochlorous acid (HClO) was known to the elder generations.
Hypochlorous acid is a good bactericide with three characteristics as follows.
- Strong and quick sterilization effect in low-concentration dosages
- Little residue; hypochlorous acid liquids rinsed with water
- No trihalomethane generated
Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) stems from hypochlorous acid (HClO) which contains hypochlorous acid ions (ClO+) accounting for 90%. (As shown in the figure (top), the sterilization curve is drawn at the top.) Hypochlorous acid ions with little sterilization effect combine hydrogen ions (the molar ratio of hypochlorous acid ions to hydrogen ions=1:9) to become hypochlorous acid for sterilization. That is, sterilization is a slow process. Thus, hypochlorous acid ions are remained significantly.
Comparatively, weak-acid sodium hypochlorite contains hypochlorous acid ions (10% only) and hypochlorous acid for sterilization mostly. Thus, sodium hypochlorite features quick sterilization effect and little residues.
Moreover, trihalomethane which is a problem related to sodium hypochlorite is generated in alkaline environment rather than acidic environment.
There are two reasons which result in hypochlorous acid unpopular.
- Difficulty in manufacturing (poor stability and diseconomy)
- Difficulty in storage
That is, hypochlorous acid is produced difficultly and not stored for a long period.
2. Hypochlorous acid is produced in electrolysis first.
There are three methods shown as follows:
- Electrolysis of saline solutions: By using salt water for producing strong acidic water but the HCLO is unstable.
- Electrolysis of saline solutions in which HCl is mixed for production of hypochlorous acid (weak acid).
- Electrolysis of water in which HCl is mixed for production of hypochlorous acid (weak acid).
Each of the methods has specific advantages but is uneconomic because of consumable platinum (titanium) electrode plates expensive.
3. Hypochlorous acid – the key element of sterilization!
Hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is similar to ozone or chlorine dioxide, is capable of resolving and killing bacteria (viruses) in oxidation. However, hypochlorous acid unlike alcohol does not induce antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
In addition, hypochlorous acid which has no toxicity of ozone or chlorine dioxide is a mild bactericide for human beings.
Hypochlorous acid (HClO) vs. sodium hypochlorite
The sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid (pH=5.2; chloride concentration=57ppm) and sodium hypochlorite (pH=9; chloride concentration=200ppm) are compared and shown in the table (below).
The sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are similar; however, the sterilization effects of hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite on Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus) and mold are significantly different.
As shown in the table, hypochlorous acid has characteristics such as good sterilization effect and fast-acting property.
| Tested strains | Microbial content | Hypochlorous acid | Sodium hypochlorite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloride concentration=57ppm; pH5.2 | Chloride concentration=200ppm; pH9 | ||||||
| After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | ||
| Escherichia Coli | 4.3x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4.5x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Bacillus subtilis | 4.6x106 | 3.7x105 | <10 | <10 | 4.4x106 | 4.5x106 | 4.5x106 |
| Aspergillus niger | 2.0x106 | <10 | <10 | <10 | 2.0x105 | 50 | <10 |
<10: no microbe detected; test temperature=23°C (Japan Food Research Laboratories)
The sterilization effect of hypochlorous acid (pH=5.2; chloride concentration=80ppm) on bacteria is shown as follows.
There is no bacterium detected after one minute.
It can be seen that all bacteria and viruses are eliminated by hypochlorous acid.
※Note: These results are test data from experiments only because hypochlorous acid reacting with other organic matters is consumed. In practice, new hypochlorous acid should be added frequently for a constant concentration.
| Tested strains | Testing liquid | Microbial content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 1 minute | After 3 minutes | After 5 minutes | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Escherichia coli | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Salmonella | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bacillus cereus | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| MRSA | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Legionella pneumophilia | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Vibrio parahemolyticus | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Campylobacter | Object | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 | 1.1x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Aspergillus niger | Object | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 | 1.0x105 |
| Hypochlorous acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
Test temperature=23°C
|
||||
4. Spraying in space:
The airborne bacteria in space will be killed by sprayed hypochlorous acid.
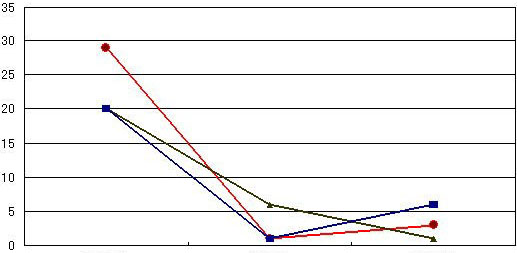
The diagram below illustrates the counts of falling bacteria within one hour in a 6-bed ward in which hypochlorous acid (200ppm) was sprayed. The data was collected in the beginning and after 30 & 60 minutes with hypochlorous acid sprayed. During the test period, nurses moved in and out the ward as usual. The counts of falling bacteria were dropped dramatically in 30 minutes with hypochlorous acid sprayed and kept almost unchanged after the next 30 minutes. The status of MRSA, which was positive before spraying of hypochlorous acid, became negative after 30 minutes.
| Counts of falling bacteria | Changes in counts of falling bacteria |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Before spraying During spraying After spraying |
5. Hypochlorous acid for deodorization:
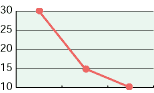
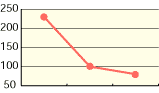
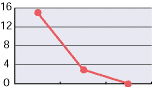
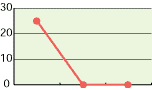
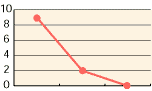
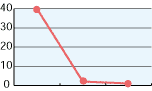
As shown in the diagrams below, hypochlorous acid is particularly effective in deodorizing organic matters. Moreover, it is necessary to deodorize the source of odors which come from bacteria mostly.
| CH3CHO | NH3 | H2S |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins |
| TMA | Methyl mercaptan | CH3COOH |
 |
 |
 |
| 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins | 0 30 mins 60 mins |
| Free effective chloride concentration in testing=80ppm | ||
In the past, the ordinary deodorant discharges aroma to restrain foul smells. Comparatively, hypochlorous acid transforms reek to odorless air through chemical reactions.
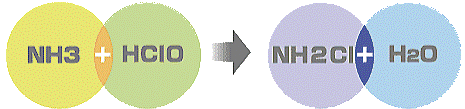
Particularly, ammonia, which is one of four major sources of foul smells, disappears as shown in chemical reactions below.
 |
||||||
| Ammonia + hypochlorous acid |
|
|||||

※ Note: The technique of sterilization based on chloramine had been adopted by some nations in Europe and Japan in the 1920’s because chloramine chemically reacts with organic matters slowly and the residual effect restrains foul smells.
Hypochlorous acid stored in ultrasonic sprayers can be sprayed in consulting rooms, operating rooms or doghouses by animal hospitals for odor control. Furthermore, hypochlorous acid is very effective in deodorization of pets’ feces.
6. Safety of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid can be created in blood of a person in whom the invading bacteria or viruses are killed. That is, our bodies are very familiar with hypochlorous acid.
Test results for animal safety with hypochlorous acid (50ppm):
| Mistaken swallow | → | Normal |
|---|---|---|
| Acute toxicity test by the single oral medicine | ||
| Skin (eye) contact | No irritation | |
| Single skin irritation test; eye irritation test | ||
| Allergy | No allergy | |
| Allergy test | ||
| Cancer | No cancer induced | |
| Mutation test in convalescence (mutagenicity test) |

 English
English  繁體中文
繁體中文  简体中文
简体中文 



